Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
The process of creating and maintaining a flourishing vegetable garden begins a long time before the actual planting of the seeds. Knowing the right moment to do it and starting seeds indoors at the right time are some of the factors that will determine whether or not one gets a bumper harvest. No matter which category of gardeners—professional ones or those who have just started—knowing the time frame for starting seedlings indoors will, without a doubt, lead to healthy plants and an easy outdoor transition when the time comes. This guide will provide you with essential tips and techniques for scheduling your planting calendar, synchronizing your indoor seeding with the natural growing season’s cycle. Be prepared to find out how right planning can cement the success of your garden!
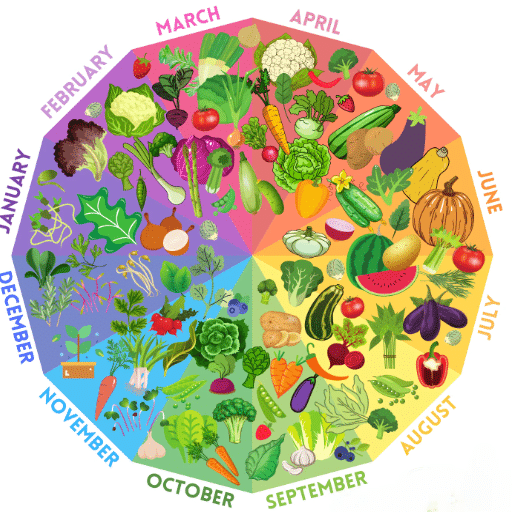
The vegetable planting calendar is a very important item for carrying out your garden activities in the right time. It tells you when to germinate seeds in the house, when to move the little plants to outside, as well as the time for direct sowing of seeds outdoors or ground based on the climatic condition and the particular vegetable’s growing season. The calendar is usually designed along the frost timelines—estimations of the last frost in the spring and the first frost in the fall—which lets you to plant according to the best conditions for each plant. Thus, by coordinating your planting with these dates, you can place your crops in the best conditions for flourishing. Always check the local area-specific recommendations to get the most accurate guidance.
A planting calendar is a very handy instrument that supports the gardeners in finding out the best periods for sowing, transplanting, and harvesting the different plants depending on their individual requirements and the local climate. It is usually arranged according to factors like frost dates and seasonal conditions, thus allowing that the plants are grown at their best times in terms of growth. Gardeners relying on planting calendars can hardly miss a successful harvest and can thus avoid losses due to bad weather or wrong timing.
In vegetable gardening, timing is very important since it directly affects the health, growth, and yield of the plants. On the one hand, sowing seeds too early risks exposing the plants to frost and freezing, while on the other hand, late planting may not allow the crops enough time to ripen before the end of the growing season. Using a planting calendar that considers the local climate and the seasonal changes helps make sure that vegetables germinate, grow, and are ready for harvest during their most favorable periods. Correct timing also reduces the risk of encountering problems such as pest infestation, diseases, and poor soil conditions, thereby increasing the chance of enjoying a successful and generous harvest.
Hardiness zones are one of the main factors that determine the kinds of plants that can flourish in a certain area, as it shows the average minimum winter temperature of that location. Growers and gardeners can take advantage of these zones to pick those plants that are already adapted to their local conditions thus, their chances of survival and growth will be higher. When they know their zone they can steer clear of the plants that would otherwise have a tough time or even die because of extreme cold or heat. In addition, hardiness zones are a great help in determining when to plant and harvest as they give clues about the length of the growing season and the timing of frost. Eventually, this knowledge contributes to maximizing of the success and productivity of any garden or crop.

Starting seeds indoors is a process that begins with the selection of a proper container that has good drainage and filling it with a seed-starting mix of high quality. Sow the seeds in the depth suggested on the seed packet, and water gently, keeping the soil moist evenly but not soaked. Put the containers in a warm place, preferably the temperature should be around 65-75°F, and make sure they get enough light—either by placing them next to a sun-drenched window or alternatively using the grow lights for 12-16 hours daily. The moment the seedlings have the first true leaves, give them a light fertilization with a diluted, balanced fertilizer for plants. Finally, adhere to a proper schedule for watering and transfer the seedlings outdoors when the conditions allow.
In the process of picking the right seeds, taking into account factors such as your local climate, soil type, and the length of the growing season. Choose seeds that are best suited not only to your region but also to your gardening ambitions, whether you want to grow vegetables, herbs or flowers. Seed packets will give you important information regarding planting depth, spacing, and sunlight requirements; therefore, checking them is necessary for successful growth. Also, based on your liking and needs, select the type of seeds you want – heirloom, hybrid, or organic. Starting your project with premium seeds from a reliable supplier will dramatically increase the odds of an impressive garden.
If you want to get started with seeds indoors the right way, you will require some necessary items that will help create the best environment possible. To begin with, pick seed trays or containers that come with drainage holes to make sure there is no standing water. High-quality seed-starting mix should be used only since it is light, and it is especially made to be beneficial for root development. In case of limited light, grow lights will be needed to keep the light levels up in that particular area. A humidity dome or a plastic cover can keep moisture levels constant while a watering can or spray bottle will provide gentle hydration. A heat mat, which is especially important for the germination of heat-loving plants, can be used to provide consistent warmth. All of these supplies will be the foundation of robust seedlings that are prepared to move into your garden.
The management of several important factors is essential to ensuring optimal conditions for sprouting. First, provide light that is adequate and consistent, either from a sunny windowsill or grow lights placed near the seedlings. Next, humidity must be kept constant and at the right level by using a humidity dome that helps with moisture retention and, furthermore, prevents the seeds from drying out. Watering should be done gently and in a controlled manner, by using a spray bottle or watering can that avoids soil disturbance. Moreover, consistent warmth derived from a heat mat is vital for the germination of plants that prefer warmer conditions. By closely keeping an eye on these factors, you will create a perfect setting for successful sprouting.

Note: Adjust the schedule based on your local frost dates and the specific needs of your plants.
Frost dates are very important for gardeners since they help in deciding the best time to plant different vegetables and flowers. The last frost date is when freezing temperatures in spring will probably stop and the first frost date is when they will probably start in fall. These dates are very crucial in determining when to start seeds, transplant seedlings, or directly sow crops outdoors so that the plants will not get hurt by frost. By knowing frost dates and changing planting schedules accordingly, gardeners can create optimal growing conditions, thus significantly improving their chances of a successful harvest. Local differences in frost dates are due to climate, elevation, and geographical location, therefore, it is important to consult regional resources or tools for accurate frost predictions.
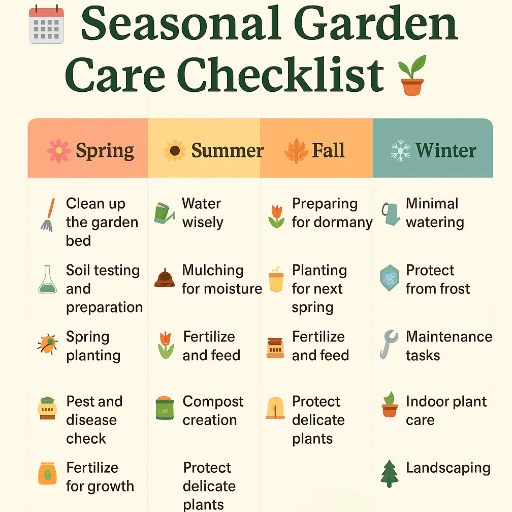
Spring planting usually starts right after the last frost date as soon as it is warm enough for seeds to germinate and plants to grow. Cool-season crops such as lettuce, spinach, peas, and radishes can be planted earlier while warm-season crops like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers should be planted later when there is no risk of frost. Fall planting is all about crops that are okay with cool temperatures, for instance, broccoli, kale, carrots, and garlic; these can be sown late summer or early fall, and they would then mature as the weather gets cooler. Timing and planning for each growing season get the plants their optimum conditions to grow and thus increase the yield.
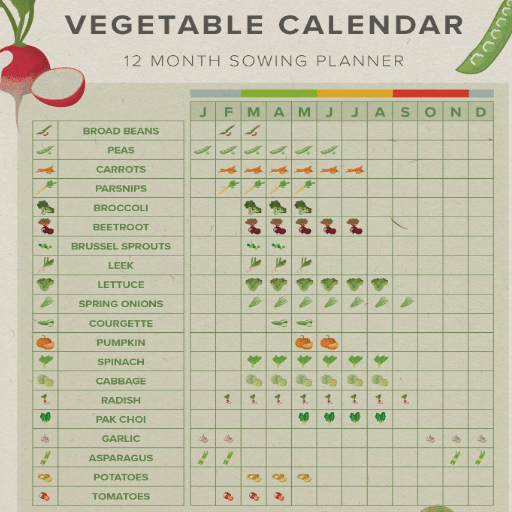
A gardening calendar is one of the most important tools to guarantee that your planting will be successful. It reminds you of key dates like when to start seeds indoors, transplant seedlings, and sow outdoors directly. If you synchronize your planting with seasonal conditions and frost dates, then you will be able to grow your plants without any hiccups. Moreover, a gardening calendar will be of help to you while planning crop rotation and successive planting for not only maintaining soil health but also for the whole year. Using this tool wisely will allow the gardener to keep his/her hands on the pulse of the garden and at the same time make smart decisions leading to a highly productive and lively garden.
If you follow these instructions, you will have perfectly healthy seedlings and a vigorous growing season opening.
Planting peas indoors is surely one only way to avant-garde them before the outdoor season of growing season starts. The seeds of peas have to be sown indoors nearly a month before the expected last frost. Take the seed trays or small pots with good-draining soil and fill it with potting soil, and then bury the seeds about an inch deep. Continuously keep the soil moist and put the trays in sunlight or under grow lights. Whenever the seedlings have grown a few inches tall and the frost threat has passed, they can be moved to the outside. Make sure that the seedlings have been hardened off for a couple of days before transplanting so that they can acclimatize to outdoor conditions.
The earliest time for starting kale seeds indoors is roughly six to eight weeks prior to the last possible frost date in your zone. This timing grants the seedlings to be established in the warm indoors prior to the outdoor transplanting when conditions are just right. The earlier the start, the stronger the plants will be and the sooner they will be ready to enjoy the warm weather once the frosty nights are over.
If you’ve decided on an indoor planting, kale is just one of the many vegetable seedlings that can be grown indoors. Tomatoes are another vegetable that is often chosen, as they are sturdy when transferred outdoors, having thus received the early start of the season. The same goes for all the varieties of peppers – both sweet and hot – which require the longer indoor growing time to yield fruits. Within the indoor-transplant period of 6-8 weeks, eggplants and broccoli can also be added to your options. Basil and parsley are examples of herbs that can be popular indoor crops. Thus, you can have fresh and dried seasonings for your kitchen every day throughout the year. By sowing these vegetables indoors, you can not only maximize your yield but also ensure a proper timing of the transfer to your outdoor garden.
Monitoring the growth of your plants involves viewing any alteration in their size, color, or health. Check for the appearance of new leaves, flowers, or roots from time to time, as these would ensure healthy growth. If there are signs like leaves turning yellow, poor growth, or wilting, then adjustments in their care routine would be appropriate. If distress signs occur, revisit factors such as lighting, watering schedule, and nutrient levels to determine if the plants’ needs are duly fulfilled. The art of adjusting the routine in response to each plant’s reaction will ensure the long-term health and growth of the plants.
Planting should be done at a particular time so that seedlings can become successfully established. Prior to transplanting, seedlings should be hardened off, reducing transplant shock by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions for about 7 to 10 days. Select a calm day, preferably cloudy, to reduce the plants’ stress due to wind and luminous sunlight. Ensure that the soil is properly prepared, nutrient-rich, and moist before planting, but never soggy. Remove the seedlings very gently from their containers so that the roots are not disturbed. Plant them at the same depth as they were growing in the pots. After transplanting, water well soasy to settle the soil and help root-to-soil contact. Continue to assess and care for the plants so they may dissipate, become acclimated, and grow well.
Planning for future planting mainly requires consideration of specific planting dates along with regional climate patterns and lunar phases that may affect growth. To have a more effective use of the almanac, determine your exact planting zone and refer to the almanac for recommendations for your area. The focus should be on frost dates when safe planting times for seeds or transplanting seedlings are established. Also, be sure to follow the suggestions on crop rotation, soil preparation, and companion planting so you can increase yields. Therefore, following the advice within your gardening activities would help in scheduling plantings and supporting long-term garden health.
Farmers’ Almanac – Planting Calendar
This source offers a planting calendar based on the Moon’s phases and positions, providing guidance on the best times for specific gardening tasks.
Farmers’ Almanac Planting Calendar
Johnny’s Selected Seeds – Seed-Starting Date Calculator
This tool allows users to input their frost-free date to calculate recommended seed-starting and transplanting dates for various crops.
Seed-Starting Date Calculator
Empress of Dirt – Indoor Seed Starting Schedule
This guide provides a detailed sowing plan for starting seeds indoors, including timelines relative to the last frost date.
Indoor Seed Starting Schedule
If you set your indoor gardening calendar to grow vegetables, you must be really sure about the best times to plant the vegetables; a usual planting calendar can vary based on yours’ USDA plant hardiness zone and the specific types of plants that you intend to grow. For instance, in zone 5, one would start growing tomato seeds indoors about 5 weeks before the last spring frost date, so that the seedlings are ready to be transplanted when the weather warms up. To tell apart when to sow seed outdoors and when to start inside, one could make use of a seed planting calendar. Remember to check with your gardening guide for exact planting dates.
Frost dates are of utmost importance in your indoor garden calendar since they specify the dates when seeds can be sown outside safely. Considering that average frost dates for your area serve as a guide for your gardening activities, please make sure you plan accordingly. The colder the zone, the farther ahead of the last frost date you must sow your seedlings indoors so that they will be ready by transplanting time. You will benefit from following your local weather carefully and shifting your planting schedules as required. The ability thus gained will definitely allow for successful succession planting, enabling at least two harvests during a growing season.
For any indoor gardening calendar, the planting guide is the mainstay. It caters to customers in terms of the recommended dates for sowing seeds indoors and transplanting outdoor seedlings. It also identifies the best time to plant specific vegetables, such as kale and arugula, depending on your hardiness zone. Along with helping you find out about companion planting so that plants grow well together, planting guides take you a step further in ensuring the success of your indoor gardening by specifying when to plant the vegetables.
Having knowledge about your zip code would be mighty helpful with creating your indoor gardening calendar. Many websites provide you with the hardiness zone of your area according to the USDA once you simply enter the zip code. This sort of information is fundamental in deciding what varieties of plants to grow and when to begin working with them indoors. For instance, you might have to concentrate on varieties that mature fast or get your plants started indoors early if you’re in an area with a shorter growing season. Your zip code should be used as a change factor in adapting your planting schedule accordingly for good climate conditions.