Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Plants are very interesting organisms, being life-sustaining organisms, and the study of plants enables a field of discovery. For any interested student, a budding scientist, or a teacher looking for stimulating activities, plant science experiments offer a perfect opportunity to explore nature firsthand. From examining plant growth and how plants react to environmental stimuli to unraveling the mystery of photosynthesis article that will lead you through fun and informative experiments is waiting! So get ready to dig in deep with plant science and enrich your knowledge with fascinating insights.

Plant growth is a result of cell division and cell enlargement, causing the plant to increase in size and develop structures. The Sun, water, nutrients, and air are some of the major forces influencing growth. Sunlight feeds the plant through photosynthesis, in which plants transform light energy into food. Water carries nutrients to cells and maintains their integrity. Nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from soil, contribute to root development and leaf formation. Air is a medium in which carbon dioxide is present, a worthy ingredient for photosynthesis. The presence of all these elements in the right balance will lead to plant growth and development.
Plants need sunlight, water, nutrients, and air to grow healthy. Sunlight gives the in energy for photosynthesis through which the plant makes its own food. Water is needed in plants for absorbing nutrients from soil and to keep the plant hydrated. The essential nutrients are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients stimulate different processes of the plant, like root development, flower development, and leaf production. Air gives carbon dioxide, the other essential ingredient with which plants carry on photosynthesis. Hence, all together these create a best environment for plant growth.
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Sunlight | Provides energy for photosynthesis |
| Water | Carries nutrients and maintains hydration |
| Nutrients (N, P, K) | Support root, flower, and leaf development |
| Air (CO₂) | Essential ingredient for photosynthesis |
Soil is an important factor for growth while acting as a main supplier of nutrients, water, and support. Some of the soil nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These ions are responsible for many physiological processes such as root elongation and flower development. They serve as water reservoirs for the plants, ensuring that plants are adequately hydrated and can move nutrients downwards more effectively. The soil structure helps anchor plants in place, providing stability to growing roots. If the soil is healthy, with plenty of organic matter and billions of microorganisms, then the plants will grow well. Such a soil atmosphere is conducive to photosynthesis since there is an exchange between gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Seeds sprout and grow through a process called germination. This begins when a seed draws in water, swelling and bursting through its outer coating. Once hydrated, the dormant embryo within the seed awakes, and enzymes start converting stored nutrients into energy. The seed first develops a tiny root, or radicle, that anchors it into the soil and begins to absorb water and minerals. Then, the shoot moves upward to grab hold of sunlight, to start the process of photosynthesis. If sufficient water, sunlight, and nutrients are all present, the seedling will carry on growing by developing leaves and gaining stronger roots to support further development.

Seeds germinate when suitable conditions have been provided. The major factors are water, oxygen, and temperature. The first act of germination is water absorption causing the seed to swell. This swelling pushes against the outer shell of the seed causing it to rupture. Subsequently, the root grows downward, embedding itself into the soil, while the shoot extends upward toward sunlight. This process allows the seedling to begin photosynthesis, enabling its development into a mature plant.
This experiment requires that we select a few healthy bean seeds to allow for their growth. Place them on a damp paper towel and store them safely in a plastic bag to keep the moisture. Then, keep this bag in a warm dark place to initiate germination. Afterward, have the seedlings planted in pots with soil; ensure they have exposure to sunlight and must be watered daily. Keep observing them for change in growth including change in height, leaf growth, and root structure and record them. The experiment honestly tells us about water, temperature, oxygen, and light conditions which the plants require for growth and development.
Stem growth is highly variable and largely depends on environmental factors such as light, water availability, and temperature. Stems exposed to sufficient sunlight typically develop by growing straight and strong as the stem seeks uniform light to carry out its photosynthesis; whereas a stem in a dimly lit environment becomes elongated and weak in a frantic attempt to grasp the nonexistent light. Water availability is yet another important factor that keeps the stem flowing with water, turgid, and maintaining its structural support. In contrast, water scarcity causes stunted growth. The temperature plays a vital role in stem growth as well; within its optimum range, growth occurs steadily, but if it deviates from this range, stem growth is adversely affected. Hence by controlling these factors in an artificial environment, the respective influences of each condition on stem growth may be studied and could be understood much better.
To answer these questions, simple experiments can be performed by students so they can see the effects of water and temperature on growth in plant stems. For example, they could grow the same plants with different watering regimes to observe how water availability affects turgidity and growth. Likewise, the plants will be grown under different temperature conditions to monitor how changes affect their growth. From these experiments, students will be able to conclude how important water and temperature are for a plant to be healthy and grow. Observations should be made systematically to sharpen the understanding of the relation between these variables and plant development.

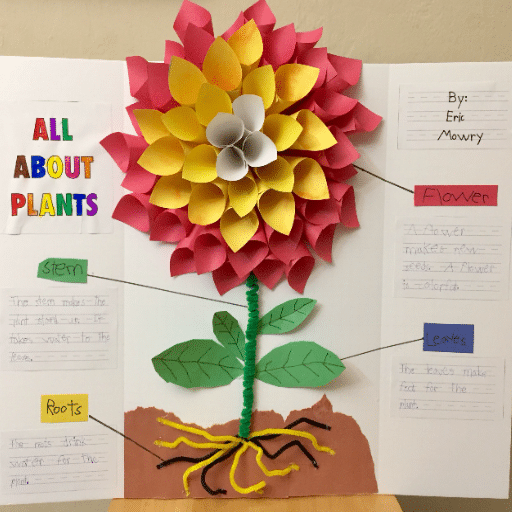
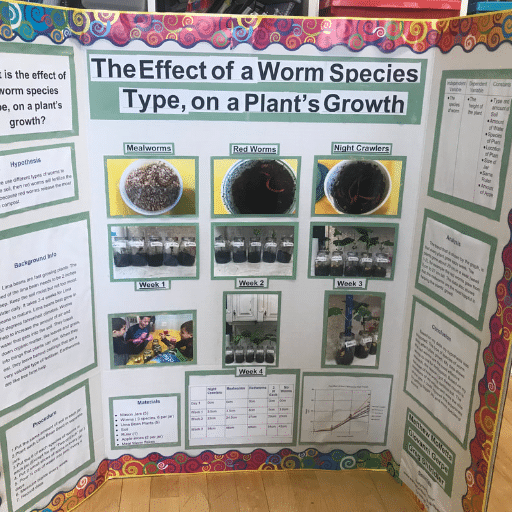
Selecting a topic for the science fair deserves great consideration. Pick something that draws you in and conforms to your level of knowledge. Delve into a topic with as much thoroughness as possible, using credible sources like educational websites, books, or scientific journals. Develop your hypothesis clearly and make sure it is something that can be tested by experiments. Give great consideration to planning out your experiment and carrying it out with care, to uphold the principles of good methodology: to collect and analyze precise data. Thereafter, you must create a project report given in neat notes, charts, and photographs to make your project sufficiently clear. Go on to prepare an exciting and well-organized presentation board that carries your hypothesis, procedure, results, and conclusion. Practice presenting your project to others confidently and clearly so that you stand a chance of answering the judges’ questions well.
Choose a plant science project according to what works for you and with the resources you have. Ask yourself questions like, “What kind of plants do I prefer to study?” or “What environmental parameters can I easily work with in my location?” Also, assess the total time required for completing the project, ensuring that the time allotted for observations and data collection is enough. Pick something simple and interesting-such as testing the effects of light, water, or soil types on plant growth. A project matched to your interest and resources is sure to lead to a fun and fruitful scientific investigation.
With your plant experiments, the first step is to state your research question or hypothesis clearly and be sure that it is related to the environmental parameters tested, such as light, water, and the types of soil. Provide a short description of your experimental procedure, mentioning the materials used, the variables that were controlled, and how long the observations were made and the data collected. Represent your findings, using charts, graphs, and photos, if necessary, to maintain clarity. It is also important to explain how the results led to the resolution of your research question and to discuss the significance of these results. The presentation should be engaging but well/she/he/it subjected to the key points and should be kept brief.
Good plant science can be shared by narrating the interesting stages of the experiment and the results. This description should begin with including something about the materials used, such as the plant species, the soil type, and the environmental setup, ensuring that the audience can comprehend the whole setup. In treatment and control, one has to mention the variables set to the constant, such as light exposure, water quantity, or temperature, and discuss the duration of observation with its timeline. Consider incorporating visuals, such as growth progress charts or photographs of the plants at different growth stages, to present your data in a manner that can be easily grasped and interpreted. Finally, end your presentation by sharing the results: Did the research resolve the initial question? Discuss results in the larger context: how could this lead to the further practice of sustainable agriculture or working toward understanding environmental change? With a clear-cut storyline, the audience will wisely relate to the significance of the study and its possible impact.
The technological boom has drastically altered the study and understanding of plant science. With tools like remote sensing, drone imaging, and satellite imaging, researchers could assess plant health, growth, and their environmental impacts on mass scales; an undertaking that was once challenging and time-consuming in a smaller context. Genetic-editing technologies have brought forth newer avenues for bettering crop resistance, productivity, and quality. Computer-based models and AI-powered analytics optimize agricultural systems, forecast growth, and recommend sustainable farming methods. Such tools and methods demystify complex plant processes, leading to a deeper understanding and practical implementation in agriculture and conservation.
Plant habitats vary universally-from rainforests and deserts to alpine meadows and coastal wetlands, each giving rise to special kinds of ecosystems. A rainforest contains gigantic trees with a dense understory of other plants; this biome requires humid weather and copious irrigation. By contrast, the desert supports plants capable of adapting to water conservation, such as cacti and succulents. Alpine meadows provide an environment for plants that can resist the cold; coastal wetlands are the homes of salt-tolerant species such as mangroves. It is through exploring these diverse habitats that one comes to know how intricately plants have been conditioned to survive and grow under different environmental contexts.
Multiple factors affect the growth of grass, so let’s review some questions pertaining to the coordination between these factors. What conditions favor grass growth? Grass grows well in loose, well-draining soils, with plenty of organic matter to feed on, and depending on rain and sunshine for life. How does temperature affect the speed at which plants grow? Usually, within temperature ranges favorable for a plant, warmer temperatures speed up some growth processes, but in extreme heat or cold, plants may slow down further. What changes does the water frequency make? This grass species needs regular watering, but on the contrary, overwatering would bring root rot and bad aeration, among other issues. By conducting some experiments with these factors, one can learn some fine points on how to best sustain healthy grass growth.
Temperature affects grass growth, and the increased warmth above what is optimal for the plant tends to encourage faster development through forming quicker metabolic mechanisms. On the other hand, extreme highs or lows stall growth or potentially harm the plant. In considering whether or not to water the grass, an important aspect about the health of the grass is maintaining a balance: too much water and dehydration set in. In proper water intervals, water seeps into the turf rooting area. However, if overwatering occurs, this can cause soil aeration to shrink along with root rot. Having a little bit of knowledge about and balancing these two factors can greatly expedite growing healthier grass.
Science Buddies – Plant Biology Science Projects
This site offers a variety of experiments focused on plant biology, including growth, photosynthesis, and adaptations.
Visit Science Buddies
ThoughtCo – 23 Plant Experiment Ideas for Science
A comprehensive list of plant experiment ideas exploring agriculture, medicine, and biotechnology.
Visit ThoughtCo
Project Learning Tree – Easy Plant Science Experiments for the Classroom
Features simple experiments like how water travels through plants and how leaves breathe, ideal for classroom settings.
Visit Project Learning Tree
Plant growth experiments in school give students exposure to and knowledge about conducting simple projects related to factors affecting growth. For instance, students may use a sunny window to grow bean plants and compare the growth of those kept in a less sunny environment. Growing seeds in baggies with wet paper towels allows students to observe germination very closely. By observing plant health and growth while altering light and moisture conditions, students can learn how these factors affect plants over time.
Roots have always been a vital feature of botany as they anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Hence, understanding the functioning of roots gives the students insight into why a plant has to grow under definite conditions. The students can even conduct experiments to study how roots draw water from their environment and how that helps keep the plant healthy. In observing roots, a clear jar filled with dirt could help the students observe growth patterns and, consequently, how, through roots, different plants get sustenance.
A wide range of science activities involving plants enhances project-based learning that provides hands-on applications to make a concept more tangible. For example, the students can experiment with planting seeds to observe their growth in two environments: one being in a greenhouse, and the other on a sunny window. This type of activity enables the student to explore scientific principles, such as photosynthesis and plant requirements for light. Another aspect to emphasize would be noting the changes over time, thus developing their analysis skills to relate to their observations as a conclusion.
Students may do projects for a science fair, looking at how plants of various kinds respond to stimuli. It can be tested how sunlight affects grass seed growth, with some pots placed in sun and others in shade. Another cool project is putting colored water into a celery stalk and timing how long it takes to turn color as a demonstration of water movement in the plant. Such projects will definitely serve as creative assignments and opportunities to market their views about plant biology.