Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
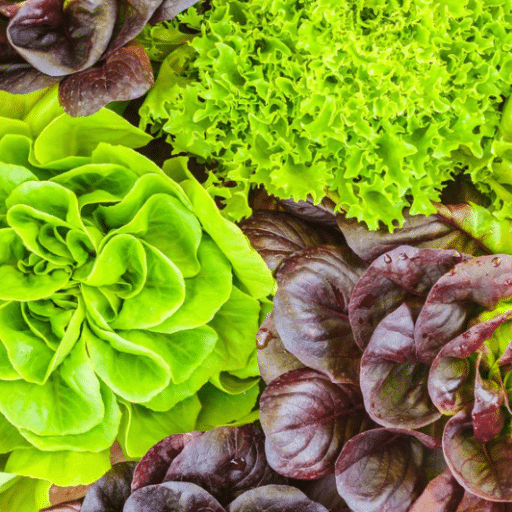

Lettuce is undeniably the champ among vegetables along with its almost unending list of culinary uses: crisp salads, gourmet wraps, and even decorative garnishes. The good thing is, with lettuce’ vast spectrum of textures, flavors, and colors, each and every one of them has its respective variety, so there is no need to worry about picking the wrong one for the dish or salad. In fact, this post will take you into a deep dive of lettuce’s amazing world such as the available varieties, their typical features, and how to grow your personal one from seed. Regardless you are a home gardener, a professional cook, or simply a lettuce lover, you will all gain precious insights and hints for your increase of this leafy green essential.
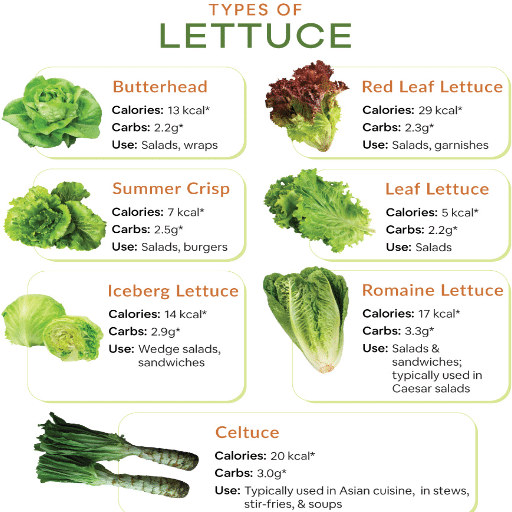
Lettuce is a widely used leafy green that is very popular and has many different usages. It belongs to the daisies family (Asteraceae) and, in fact, is in the top of the list of salad ingredients. However, it is also used in wraps, sandwiches, and even in cooking. The topmost categories of lettuce are romaine, iceberg, butterhead, and loose-leaf, all of them having their own individual textures and tastes. Being rich in vitamins A and K and low in calories is the reason why lettuce is considered a very nutritious food. It is also capable of thriving in cooler conditions and it needs well-drained soil, making it a preferred choice among backyard gardeners. Because of its fast growth and versatility in cooking, lettuce has become a regular in kitchens around the globe.
Lettuce is a salad-type vegetable that is very often used as the main ingredient in salads, sandwiches, and wraps. It has a wide range of varieties such as romaine, iceberg, butterhead, and loose-leaf, each of the bringing its own textures and flavors to the table. Being low in calories and a rich source of vitamins A and K, lettuce is very much regarded for its nutritional value. It is a very adaptable and quick-maturing crop that flourishes in cooler climates and the reason why it is very popular with home gardeners and has become a staple globally in kitchens.
Their crispness, refreshing taste, and excellent dressing and toppings compatibility make lettuce the main foolproof salad ingredient every time. By providing a healthy base, lettuce, Vitamins and hydration, is still very light and low-calorie option for all the meals one would want to call healthy. It can simply combine with veggies, fruits, proteins, and grains, thus salads can be that all-encompassing and customizable to the consumers’ likings. Not only does lettuce effectively increase the salads’ aesthetic value with its different shades of green, it also provides both aesthetic and nutritional advantages at the same time.
Leafy greens are one of the most versatile and nutritious of all the vegetables and pot herbs; this is why their uses in the kitchen range over a large variety of culinary activities. They are always there in fresh salads, where their textures and tastes are added, and where they usually act as a base for other ingredients. Leafy greens are still very often added to smoothies to give an extra supply of vitamins and minerals. They also find their way into the cooking of stir-fries, soups, and casseroles, or they may simply be steamed or sautéed as a side dish, which is the simplest application of all. Being able to support and pair well with all kinds of cuisines, makes them indispensable in the composition of harmonious and appetizing dishes.
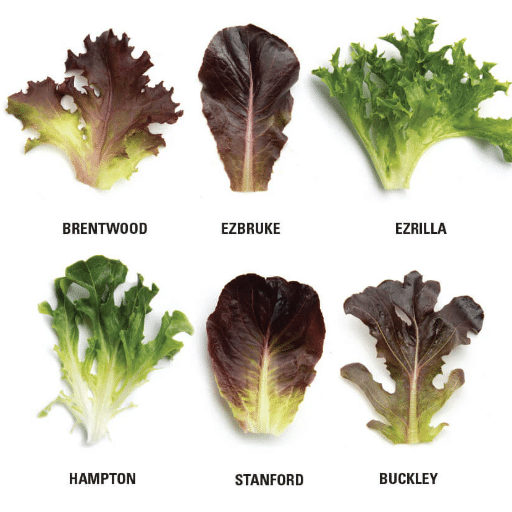

Romaine Lettuce
Romaine lettuce has a refreshing and slightly bitter taste; the robust texture of the lettuce brings it to the salads and wraps of Caesar.
Iceberg Lettuce
Iceberg lettuce has a gentle taste and a crunchy texture which make it great for salads, burgers and sandwiches.
Butterhead Lettuce
Butterhead lettuce, which includes Boston and Bibb varieties, is tender and somewhat rich in taste, thus being a good choice for wraps and salads with dressing done directly before serving.
Leaf Lettuce
Leaf lettuce is available in green and red colors, with very tender texture and slightly sweet taste. It is used mainly in salads and as a garnish.
Arugula
Arugula is a peppery green which is not considered a true lettuce but is usually ranked among the salads and pizzas.
The different types of leaf lettuces consist of green leaf as well as red leaf mostly with their respective characteristics and flavor profiles being very much alike. The gentler the flavor, the softer the texture, thus green leaf lettuce is usually recommended for salads with dressing since its sweetness blends well with other toppings. The red leaf lettuce is a good alternative for soups and stews; its tender texture and richness in vitamins make it pleasant for any dietary plan.
In the spectrum of greens, romaine lettuce is an extremely nutritious and multi-purpose vegetable, besides its distinction of being crunchy and having a very mild, almost sweet flavor. It is the favorite for Caesar salads because of the way its thick and sturdy leaves not only hold up the weight of the sauce but also bite back with crunch. The lettuce’s low-calorie contention makes it a perfect component in a balanced diet that guarantees at the same time, nourishment and satisfaction of the palate.
When compared, iceberg and butter lettuce are absolute opposites in terms of texture and health value. Iceberg is the salad ingredient synonymous with crunch and has the most attractive pale green, tight lettuce leaves. In addition, it is a lettuce variety that provides the least nutrients among all and offers only a few vitamins and minerals when compared with other lettuces. Butter lettuce, on the contrary, doesn’t lack in nutrients and has soft, delicate leaves with a slight buttery taste. It is packed with nutrients like vitamin K, vitamin A, folate, and its delicate texture is equally well suited for light dressings or fillings in wrappers. Iceberg is great when it comes to texture, but butter lettuce is definitely the one giving a more nutrient dense option.
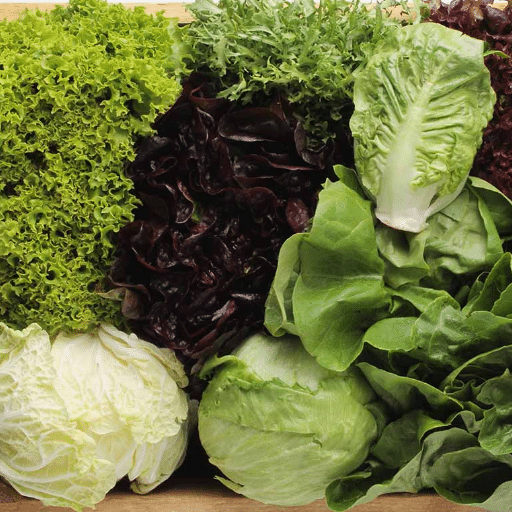

Growing lettuce can be a simple and rewarding experience when you follow a few careful steps from seedling to harvest. One of the most important things to do is to plant seeds that are of good quality and suited to your climate and growing season. Temperature is a critical factor in the life cycle of lettuce as it prefers the cool season with temperatures between 60°F and 70°F being perfect for it. Lettuce needs well-drained, fertile soil with a pH range of 6.0-7.0. Seeds can be sown directly into the soil or started indoors where they will be planted about 1/4 inch deep. Water consistently without flooding, and if you are in a warmer area, ensure that your seedlings get either full sun or partial shade. To keep your plants healthy and stimulate the ongoing production of leaves and heads, harvest the mature ones regularly.
It is important to take into account the growing conditions in your area and the type of lettuce you want when selecting lettuce seeds. Varieties of lettuce are usually divided into four major groups: crisphead, butterhead, loose-leaf, and romaine. Crisphead varieties, such as iceberg, need cool temperatures and have longer growing seasons, while loose-leaf and butterhead lettuces are not picky and can be harvested very quickly. Romaine is somewhere in between as it can be grown in warm weather as it is sturdy. Besides, the future of your garden will depend largely on your choice of seeds. Hence, always go for disease-resistant cultivars and if possible choose non-GMO or organic seeds. Moreover, always check the seed packet information for the best planting times, spacing requirements, and other care instructions to ensure easy and successful cultivation.
Seed Selection: Start by picking the best lettuce variety according to your climate and growing conditions. Check the seed packet for information about disease resistance, planting periods, and spacing requirements. Get organic or non-GMO seeds when possible, as they will be sustainable.
Site Preparation: Find a place for planting with good, fertile soil that drains well and has either full sun or partial shade. Check the soil pH, and the target is 6.0-7.0. Mix soil with compost or organic matter to enhance nutrient availability.
Planting: In case of direct seeding, place the seeds ¼ inch deep. Follow the guide for your selected variety for the distance to be maintained between the seeds. For seedlings, be careful not to hurt the fragile roots when transplanting. Remove the weak seedlings in crowded places to allow the strong ones to grow.
Watering: Keep up regular watering to maintain even soil moisture and prevent dryness. Mulching can also retain soil moisture and keep the temperature constant.
Maintenance: Always inspect the plant for any pests or diseases and use organic pest control methods where necessary. Weed the garden regularly to keep the plants free from competition for resources.
Harvesting: When the lettuce is of the right size cut it into pieces or take out the whole head and make sure rapid consumption or storage, since it cannot last long. For constant yield, plan to plant every turn.
The first thing to do when harvesting lettuce is to know when the plant is at its best maturity, and normally this is indicated by the heads of the crisp-type varieties being firm or the leaves of the leaf types being large and soft. Cut the heads or outer leaves, leaving the inside for growth, using a clean and sharp knife or scissors. It is best to harvest in the early morning when the heads are firmest and the moisture content is highest because this will help in keeping the lettuce fresh and also reduce wilting. After harvesting, the lettuce should be rinsed well with cool water to get rid of dirt and pests. Once the lettuce is harvested, it should be stored in a refrigerator where there is high humidity and low temperature between 32–36°F will be perfect for maintaining the quality and extending shelf life. Keep handling to the minimum to avoid bruising and to ensure maximum presentation quality.

Salad greens encompass numerous types, each of which brings along its specific taste, texture, and nutritional advantages. The frequently used ones are:
Romaine Lettuce: Crunchy and a little sweet, perfect for Caesar salads and tacos.
Spinach: Delicate leaves having a light, earthy taste, full of iron and vitamins.
Arugula: Spicy and fragrant, used frequently to give salads a strong flavor.
Kale: Strong and full of nutrients, excellent for cold salads or mixed with dressing to make it nice and soft.
Butterhead Lettuce: Tender, thin leaves with a very slight sweet taste, which consists of Boston and Bibb varieties.
Radicchio: Leaves that are red and bitter which provide a pop of color and a sharp, zesty taste at the same time.
Due to each type’s versatility in culinary applications, it becomes easy to prepare a salad that is just right for different tastes and dietary preferences.
Endive, a chicory family member, possesses the crispness of its texture along with a somewhat bitter taste, which, in turn, makes it widely used in raw and cooked dishes. The leafy vegetable is available in two major types curly endive (frisée) having finely serrated leaves and a strong bitterness, and Belgian endive having smooth pale-colored leaves with milder taste. Its robust quality enables it to retain full flavor in salads, appetizers, and braised preparations. Endive is a nutrient powerhouse, being a good source of vitamins A and K, fiber, and thus helping with both vision and digestion.
Spring mix or mesclun is a colorful mix of baby, soft greens which normally consists of lettuces, arugula, spinach, and field greens. This mixture aims at offering a range of tastes, textures, and colors that goes from mild, crisp to peppery, robust. The particular kinds in a spring mix differ with the seasons and the producers; for instance, red oak, baby kale, chard, and other special greens are frequently included. Spring mix is known for its easy and varied use, also being the main ingredient in salads or dressing. It is an excellent option nutrient-dense with vitamins A, C, and K, besides antioxidants and dietary fiber.
The Little Gem is a specialty lettuce that is highly regarded for its small size, crunchy texture, and sweet buttery taste. The Little Gem is a cross between the romaine and butterhead lettuce, inheriting the robust character of romaine and the soft nature of butterhead. Little Gem is enchantingly flexible, frequently found in salads, sandwiches or even in low-carb dishes as replacement of bread. Trees that are stiff yet soft are suitable for dressing and toppings without wilting, thus making it a favorite among chefs and home cooks alike. Besides its vitamins A and K, it is also a source of dietary fiber and antioxidants that promote health while improving culinary possibilities.
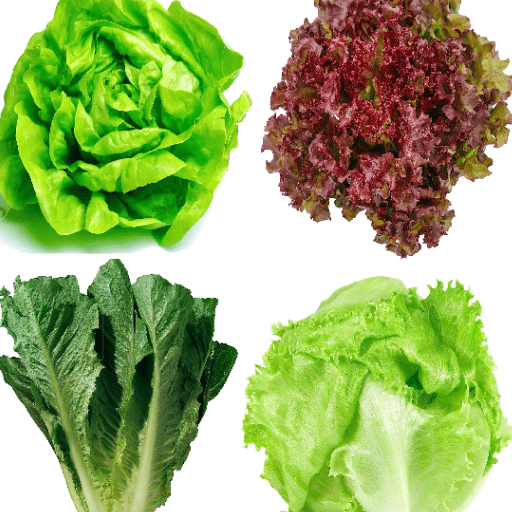

Effective management of lettuce crops involves a systematic approach giving different treatments to soil quality, irrigation, pest control, and harvesting techniques:
Soil Preparation: Make use of the soil which is nutrient-rich, well-drained, and has a pH of 6.0 to 6.5. Add organic matter to the soil so that its fertility can be increased.
Irrigation: Keep Moisture levels consistent by either using drip irrigation or sprinkler system. Do not overwater as it may cause root rot.
Pest Management: Keep an eye open for the common pests like aphids and caterpillars by frequent checking. Go for the IPM (Integrated Pest Management) practices which may include the release of natural enemies or utilizing the approved biocontrol methods.
Harvesting: Lettuce should be harvested very early in the morning when the temperature is low, so as to keep it fresh. Carefully cut the heads or leaves at the soil line without injuring the remaining plant.
Always practice these steps if you want to grow the healthiest, finest quality lettuce while at the same time facing minor hassles.
Absolutely right that in order to keep healthy leaf types, proper cultural, environmental, and pest management practices should be applied. Make sure soil conditions are right by keeping a pH of 6.0 to 6.5 and providing consistent, adequate moisture, and do not let it exceed. Spacing of plants keeps air circulation going and thus lowers the risk of fungal diseases. Fertilizer application should be done at the right time and in the proper amounts. In the early days of growth, nitrogen should be the main nutrient, but be careful not to add too much, or plants may become less vigorous and more prone to pests. Monitoring for the pests like aphids and caterpillars should be done regularly so that the pest management could be done at the right time by using IPM techniques like release of natural enemies or chemical treatments. It would be easier for the growers to maintain their plants’ vitality and to produce good quality leaves continuously if they impose such practices.
Lettuce is a cool-weather plant that grows best at temperatures around 60°F to 70°F, thus making it perfect to plant in spring and autumn. Very hot weather may lead to bolting which is a process whereby the plant turns to flowers and seeds before it has matured, and this would have a negative impact on leaf quality. To prevent this, planting heat-resistant varieties and maintaining soil moisture are the two important practices one should do in the summer season. The same soil that is well-drained and rich in nutrients with a pH of 6.0 to 7.0 is also the one that lettuce prefers to grow in. If the winters in the area are very harsh, then, planting in cold frames or using row covers will prolong the growing season and thus allow production to be continuous. Timing and variety selection are the two crucial factors to consider if one wants to produce the highest yield of quality products all year round.
Lettuce grows in a wide array of varieties, each exhibiting specific traits and tastes. Among the most common types are head lettuce, romaine, iceberg, and loose-leaf varieties. Cos lettuce, which is usually recognized by its long leaves and crunchy texture, remains a salad favorite. Moreover, butter lettuce and summer crisp varieties attract many consumers because of their soft leaves. Every kind of lettuce may be cultivated for its leaves and provide a different flavor to dishes, thus making them versatile for the culinary art. Therefore, recognizing these varieties can aid the cultivators in picking the most suitable lettuce plants for their particular requirements.
The cultivation of lettuce can be practiced in seasons, with some varieties resisting freezing while others thriving under hot conditions. As an illustration, romaine and loose-leaf lettuce may be planted in early spring and then gathered during the colder months. Alternatively, summer crisp varieties can be harvested in summer due to extreme heat. It is essential to pick the appropriate lettuce for each season to get a good yield. Moreover, clever planning allows for lettuce to be grown throughout the year, utilizing shade cloths in the summer and row covers in winter, for example. Thus, the homegrown lettuce can be taken at the freshest peak no matter what season it is.
Several factors determine lettuce seed germination: temperature, moisture, and light. Generally, lettuce needs cool conditions to germinate properly. Heat can cause premature bolting, and plants will turn bitter before reaching their full size. Sufficient water is very important because dry soil can delay germination. On the other hand, ensuring sufficient light encourages seedlings to grow true leaves faster. Knowledge of these factors can vastly increase the probability of getting lettuce crops from seeds, be it in the garden or in pots.
Romaine and iceberg are the two most popular lettuce types but they show a great deal of contrast as well. Romaine comes with long, upright leaves that are very dark green and crunchy, which makes them a perfect fit for salads and wraps. On the other hand, iceberg has a round head, and its tightly packed, crunchy leaves are usually light in color. Romaine is the flavorful one and is the one often picked because of its health benefits. Iceberg, though not harmful, is mostly just water and thus has fewer nutrients. Both types are very important in the lettuce business and are suitable for many different cooking methods.
You are a beginner gardener and want easy-to-grow lettuce varieties? Loose-leaf and butter lettuces make it through hardship very easily and are perfect for you as they are beginner-friendly. Quickly germinated, these lettuces can be harvested several times and by just picking the outermost leaves. Summer crisp and cos varieties are also easy to grow, so they are perfect for your home garden. They are tolerant to different growing conditions and do not require any specific care that novice gardeners are not already giving. Provided the correct care, these easy-to-grow lettuces can keep serving the gardener with fresh greens all through the growing season.
Production of lettuce swings widely from one area to another depending mainly upon the climate, soil type, and growing methods. Summer lettuce varieties flourish in hot regions while regions with cooler climates may concentrate on winter salad crops only. The commercial sector of the lettuce industry usually sticks to varieties that are good producers under the prevailing conditions. The areas that enjoy long growing seasons can have multiple crops each year thereby increasing their lettuce production. Furthermore, the types of lettuce being favored by the market in the area, for example, romaine or iceberg, directly affect what will be sown. Knowing these differences between regions can allow easier and more effective breast-feeding of the lettuce crops.